Approfondisci l’interazione uomo-macchina: tecnologie avanzate, AI e soluzioni per migliorare l’esperienza utente.
Patent infringement detection usually implies research among documents in different forms, in both natural and unstructured language, often involving a lot of human resources and time.
Interactive public displays have been exploited and studied for engaging interaction in several previous studies.
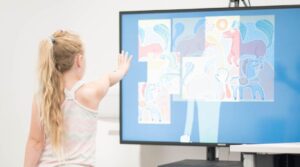
During the last decade, touchless gestural interfaces have been widely studied as one of the most promising interaction paradigms in the context of pervasive displays. In particular, avatars and silhouettes have been proved to be effective in communicating the touchless gestural interactivity supported by displays.
Touchless gestural interaction has been widely studied and adopted in many contexts. Furthermore, the growing availability of low-cost enabling devices, such as Kinect or Leap Motion, boosted up the interest in such interaction both for commercial and scientific purposes, both for large public displays and for personal displays.
Reports on the 7th ACM International Symposium on Pervasive Displays that took place from June 6-8 in Munich, Germany.
Virtual Reality (VR) is more accessible than ever these days. While topics like performance, motion sickness and presence are well investigated, basic topics as VR User Interfaces (UIs) for menu control are lagging far behind.
The use of plants as a mean for both visualization and interaction has been already explored in smart environments. In this work, we explore the possibility of constructing a controllable dynamic plant-based display using thigmonastic plants, i.e. plants that change the shape and position of their leaves as a response to external stimuli.
In this paper, we shortly introduce our idea of a sound-based system to overcome the display blindness, and some experiments that we are carrying out in order to test its effectiveness.
Many prior works investigated the potential of pervasive technologies and interactive applications to increase access capabilities to digital content for people with disability, particularly Neuro-Developmental Disorders (NDDs).
I sistemi touchless possono favorire lʹindipendenza di pazienti a mobilità ridotta nellʹaccesso ai sistemi informativi, e quindi la prevenzione terziaria.